Appearance
http缓存
浏览器缓存过程
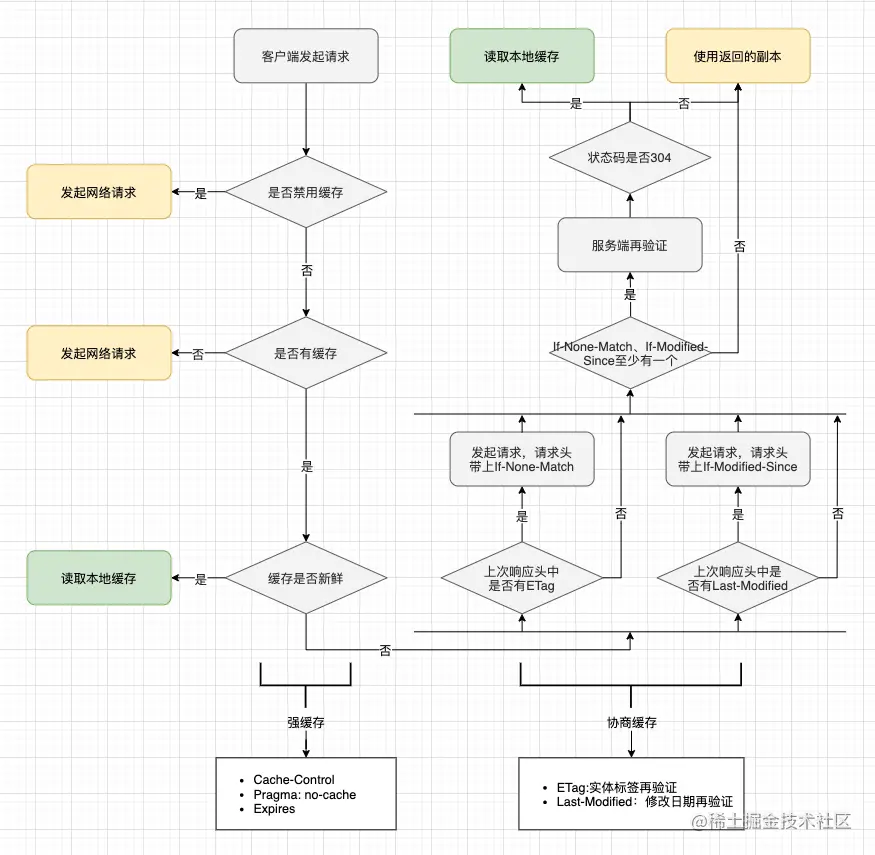
可以看到浏览器缓存判断过程,从左上到左下,是读取本地缓存的过程。通过Cache-Control判断是否禁用缓存
强缓存
Cache-Control
容易混淆的值
| 值 | 使用场景 |
|---|---|
| no-cache | 协商缓存验证 |
| no-store | 不使用任何缓存 |
| must-revalidate | 一旦资源过期(比如已经超过max-age),在成功向原始服务器验证之前,缓存不能用该资源响应后续请求。 |
通过Expires或Cache-Control:max-age=毫秒等具有过期时间的http头判断缓存是否过期(新鲜)
Expires和max-age
协商缓存
在缓存过期(Expires: Tue, 28 Feb 2022 22:22:22 GMT或Cache-Control: max-age=3600之类的时间已过期)、配置为走协商缓存的情况(Cache-Control: no-cache或Cache-Control: max-age=0, must-revalidate)
ETag和If-None-Match
浏览器请求的时候会将ETag放在If-None-Match。将由源服务器判断,ETag是否改变,决定是返回新内容200还是304状态码
Last-Modified和If-Modified-Since
http
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 1024
Date: Tue, 22 Feb 2022 22:22:22 GMT
Last-Modified: Tue, 22 Feb 2022 22:00:00 GMT
Cache-Control: max-age=3600
<!doctype html>
…以下响应在 22:22:22 生成,max-age 为 1 小时,因此你知道它在 23:22:22 之前是有效的。
到 23:22:22 时,响应会过时并且不能重用缓存。因此,下面的请求显示客户端发送带有 If-Modified-Since 请求标头的请求,以询问服务器自指定时间以来是否有任何的改变。
http
GET /index.html HTTP/1.1
Host: example.com
Accept: text/html
If-Modified-Since: Tue, 22 Feb 2022 22:00:00 GMT接下来的流程就跟ETag和If-None-Match的流程一样的